Paper Pulping Process Introduction
Paper has come a long way before it began to be manufactured in the form in which we now know it. Invented in China, from the very beginning it was an important medium of information, back then silk and linen fibers were used in its production. Currently, the starting material for the production of cellulose pulp, from which paper is made, are various types of fibrous plant materials obtained, among others, from coniferous and deciduous trees, but also from other plants, e.g. from flax, bamboo or cotton.
In the next stage, the fibrous material undergoes further processing, where it is converted into pulp, which is next processed into paper. The production of pulp can be held by mechanical or chemical methods. In the chemical pulping process, alkali (e.g., sodium hydroxide in the form of a lye or caustic soda) is usually used to remove the lignin that binds the fibers.
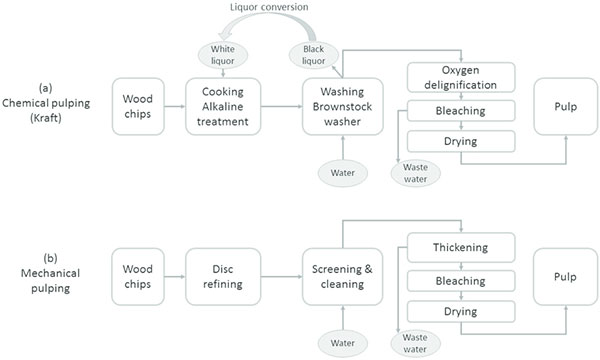
Chemical methods of pulping
Chemical pulping processes mainly consist of the use of various chemical reagents as well as heat to soften the lignin. As a result, it is dissolved and then mechanically refined to separate the fibers. In practice, two different chemical pulping processes are used.
The kraft process consists of combining wood chips with white liquor (it is an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulphide). Under conditions of elevated pressure and temperature, this solution dissolves lignin, releasing cellulosic fibers. After completing the digestion reaction, a black liquor and cellulose pulp is obtained. The liquor contains dissolved organic substances that are recovered and can be used in the chemical process again. Lignin is removed from the mass in the process of oxygen delignification (in the presence of oxygen and sodium hydroxide). The material obtained in this way is bleached in order to achieve appropriate performance, such as strength, brightness and purity of the final product.
The second process of chemical digestion is the sulphite process. It consists of using an aqueous solution of sulfur dioxide in the presence of alkalis (e.g. calcium, magnesium, sodium and ammonium). The products obtained in this process are lighter and easier to whiten, however, they have much lower strength compared to the more frequently used sulphate pulping. The sulphite process also requires careful selection of wood raw material – this method is intolerant, for example for pine wood. The sulphite process compared to kraft pulping is more efficient, produces less unpleasant gases and also allows to obtain a very light pulp, which is easily leached. Unfortunately, due to the lower fiber quality, higher energy consumption and low recoverability of the chemical raw materials used in the process, sulfite technology has been replaced by the kraft process.
Mechanical methods of pulping
Mechanical pulping provides a very high yield of pulp from wood. The main processes used on an industrial scale is the process of stone groundwood pulping (SGW), the thermomechanical pulping (TMP) and chemo thermomechanical pulping (CTMP) process.
The improvement of the SGW method is the thermomechanical pulping (TMP). In the TMP process, wood chips are initially washed to remove sand, stones and other hard impurities, then heated by steam under increased pressure, and further pulped in a disc mill. In the next stage, the mass is transported to the vat, where straightening and elimination of deformation of the fibers takes place. Finally, it is directed to the storage tank. In order to reduce the amount of harmful resins formed in the TMP process, similar chemicals are used as in the SGW process. The mass created in this way is most often used for the production of newsprint.
The CTMP process combines the TMP process together with the chemical impregnation of chips. In the first phase, they are washed and sieved and then impregnated. Depending on the type of wood, appropriate chemical solutions are used. Sodium sulphate is usually used for softwood, while alkaline peroxides are usually selected for hardwood. After the impregnation process is complete, the chips are heated and mixed with water, which loosens the lignin bonds and releases the fibers. The CTMP process allows to obtain clean pulp with sufficient strength and appropriate optical properties. CTMP is mainly used for the production of fibrous components of paper pulp, which can be used for the production of printing and hygiene papers.
Get In touch Now!
Leave messages for quotations and solutions. The average response time is up to 24 hours. Your privacy is protected. Check privacy policy here.
